New Method To Map Wildfire Fuel Types For Improved Risk Management
by Anna Sinisalo | Published: 23-Jan-25 | Last updated: 23-Jan-25 | Tags : INFRA Remote Sensing research wildfire | category: NEWS
To assess wildfire risks and develop effective strategies for reducing and managing wildfires, it is crucial to understand what fuels them. The recently published Arctic PASSION research introduces a new methodology for mapping fuel types using remote sensing data.
The frequency and extent of wildfires in the Arctic have increased in recent decades. Additionally, the timing and duration of these fires have shifted. One of the key factors influencing this is the change in vegetation, which serves as the natural fuel for the fires.
“The proposed method is cost-effective and easy to access, relying on freely available sources. Additionally, the fuel-type classification we employed can be relatively easily customized and refined for specific territories by incorporating Indigenous knowledge, thereby enhancing accuracy at local or regional scales,” says Enrica Nestola, the lead author of this study from the National Research Council of Italy (CNR).

Enrica Nestola, the lead author of the study. Photo by G. Sgrigna
Fuel type is a critical element in predicting wildfire behavior and accurate fuel-type mapping is essential for characterizing wildfire risk. Given the dynamic nature of vegetation, the ongoing impacts of climate change, and extensive land use, fuel types can change over time. Therefore, it is important to regularly update fuel-type maps.
Historically, creating fuel datasets has been a time-consuming and costly process. As a result, these datasets were not always updated frequently, posing challenges when used for wildfire behavior modeling or active wildfire management. In this sense, remote sensing technologies have revolutionized fuel-type mapping in the last fifty years.
The new methodology developed in Arctic PASSION, which uses MODIS MCD12Q1 land cover data, has the key advantage of providing annual updated fuel-type maps. In a case study of Canada, this approach achieved over 85% accuracy in classifying fuel types, and the methodology can be broadly applied to ecosystems across the boreal region.
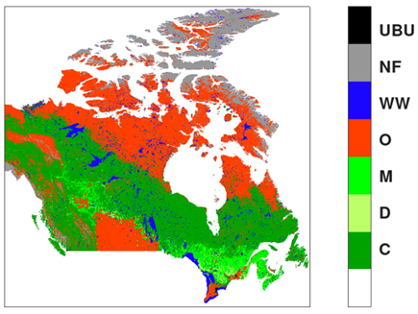
New Canadian fuel-type map presented in the study (Nestola et al. 2024).
These annual fuel-type maps are currently being integrated as an informational layer in our web-based wildfire risk management service INFRA. This integration enhances the service, making it a valuable resource for advancing wildfire monitoring and management strategies.
The methodology developed in this study can also be applied to meet the ongoing needs of national and international environmental protection agencies, as well as forestry and environmental managers.
Read more about how the Integrated Fire Risk Management (INFRA) Service works our news.
Reference: Nestola, E.; Gavrichkova, O.; Vitale, V.; Brugnoli, E.; Sarti, M. Characterization of Fuel Types for the Canadian Region Using MODIS MCD12Q1 Data. Fire 2024, 7, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7120485
